How to Trade Forex for Beginners
What is forex trading?
Forex trading is the process of speculating on currency prices to potentially make a profit. Currencies are traded in pairs, so by exchanging one currency for another, a trader is speculating on whether one currency will rise or fall in value against the other.
The value of a currency pair is influenced by trade flows, economic, political and geopolitical events which affect the supply and demand of forex. This creates daily volatility that may offer a forex trader new opportunities.
Online trading platforms provided by global brokers like FXTM mean you can buy and sell currencies from your phone, laptop, tablet or PC.
What is an online forex broker?
An online forex broker acts as an intermediary, enabling retail traders to access online trading platforms to speculate on currencies and their price movements.
Most online brokers will offer leverage to individual traders, which allows them to control a large forex position with a small deposit. It is important to remember that profits and losses are magnified when trading with leverage.
FXTM offers a number of different trading accounts, each providing services and features tailored to a clients' individual trading objectives.
Discover the account that's right for you by visiting our account page. If you're new to forex, you can begin exploring the markets by trading on our demo account, risk-free.
Why trade forex?
Forex offers many benefits to retail traders.
You can trade around the clock in different sessions across the globe, as the forex market is not traded through a central exchange like a stock market. This means you can jump on volatility, wherever it happens. High liquidity also enables you to execute your orders quickly and effortlessly.
Trading forex using leverage allows you to open a position by putting up only a portion of the full trade value. You can also go long (buy) or short (sell) depending on whether you think a forex pair's value will rise or fall.
Forex trading offers constant opportunities across a wide range of FX pairs. FXTM's comprehensive range of educational resources are a perfect way to get started and improve your trading knowledge.
Understanding Currency Pairs
All transactions made on the forex market involve the simultaneous buying and selling of two currencies.
This 'currency pair' is made up of a base currency and a quote currency, whereby you sell one to purchase another. The price for a pair is how much of the quote currency it costs to buy one unit of the base currency. You can make a profit by correctly forecasting the price move of a currency pair.
FXTM offers hundreds of combinations of currency pairs to trade including the majors which are the most popular traded pairs in the forex market. These include the Euro against the US Dollar, the US Dollar against the Japanese Yen and the British Pound against the US Dollar.
The table below looks at the most traded currency pair in the forex market.

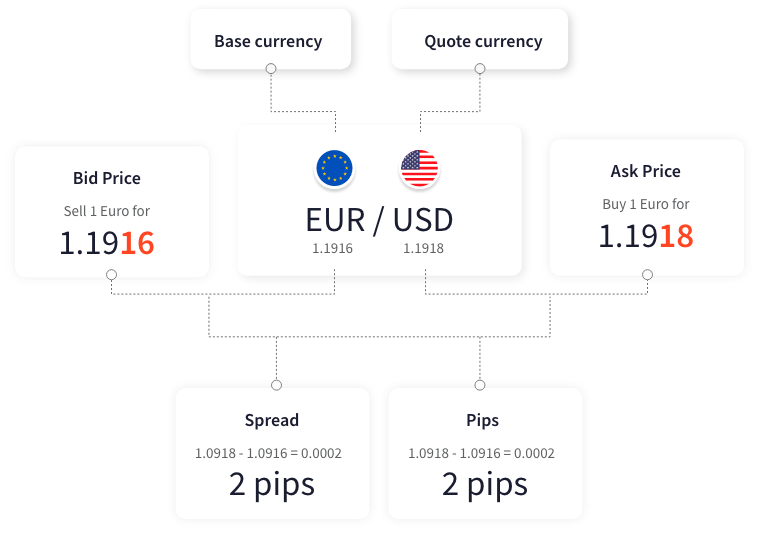
For most currency pairs, a pip is the fourth decimal place, the main exception being the Japanese Yen where a pip is the second decimal place.
On the forex market, trades in currencies are often worth millions, so small bid-ask price differences (i.e. several pips) can soon add up to a significant profit. Of course, such large trading volumes mean a small spread can also equate to significant losses.
Trading forex is risky, so always trade carefully and implement risk management tools and techniques.
What are the most traded currency pairs on the forex market?
There are seven major currency pairs traded in the forex market, all of which include the US Dollar in the pair.
You can also trade crosses, which do not involve the USD, and exotic currency pairs which are historically less commonly traded (and relatively illiquid). This means they often come with wider spreads, meaning they're more expensive than crosses or majors.
Major currency pairs
Major currency pairs are generally thought to drive the forex market. They are the most commonly traded and account for over 80% of daily forex trade volume.
There are four traditional majors – EURUSD, GBPUSD, USDJPY and USDCHF – and three known as the commodity pairs – AUDUSD, USDCAD and NZDUSD.
These currency pairs typically have high liquidity, which means they tend to have lower spreads. They are associated with stable, well managed economies and are less prone to slippage, where the expected price of a trade differs from the price the trade was executed at.
Cross currency pairs
Cross currency pairs, known as crosses, do not include the US Dollar. Historically, these pairs were converted first into USD and then into the desired currency - but are now offered for direct exchange.
The most commonly traded are derived from minor currency pairs and can be less liquid than major currency pairs. Examples of the most commonly traded crosses include EURGBP, EURCHF, and EURJPY.
Exotic currency pairs
Exotics are currencies from emerging or developing economies, paired with one major currency.
Compared to crosses and majors, exotics are traditionally riskier to trade because they are more volatile and less liquid. This is because these countries' economies can be more susceptible to intervention and sudden shifts in political and financial developments.
How to Trade Forex for Beginners
Source: https://www.forextime.com/education/forex-trading-for-beginners

0 Response to "How to Trade Forex for Beginners"
Post a Comment